
In recent years, several types of treatment for male impotence have been available. They must be prescribed by a doctor after a complete medical examination.
What are the treatments for erectile dysfunction?

There are several oral treatments for erectile dysfunction, available on prescription. They must be taken at the latest between 20 minutes and one hour before sexual intercourse.
These medications are not currently reimbursed by Health Insurance. There are also local treatments that are used just before sexual intercourse. They are administered by the patient himself, in the urethra in the form of a gel or directly into the penis by injection.
Oral drugs of local action
Oral treatments for erectile dysfunction work by promoting the filling of the penis with blood. These are avanafil (SPREDA), sildenafil (VIAGRA and its generics ), tadalafil (CIALIS and its generics ), and vardenafil (LEVITRA and its generics ). They act quickly, but only in the presence of sexual arousal. Their duration of action varies depending on the medication (from 12 to 36 hours).
These medications must be used with great caution in people with heart problems. A clinical examination of the state of the heart and blood vessels is essential before prescribing them. Only your doctor can know if you can benefit from this type of treatment. It can be dangerous to share your medication with another person.
Their most common side effects are headaches, facial flushing, a feeling of a blocked nose, dizziness, and digestive and vision disorders (blurred vision or changes in color perception). Warning: these drugs are incompatible with treatments for angina pectoris from the vasodilator family ( angina ) and with taking amyl nitrite (a sexual stimulant also called “poppers”, “boosters” or “snappers”). Their simultaneous use can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure ( hypotension ) which can lead to death.
Drugs for penile application or intracavernous injection
There are also treatments for erectile dysfunction in the form of a cream to be applied to the tip of the penis or injected into the penis. They contain a substance (alprostadil) that acts locally by causing the blood vessels in the penis to dilate, thus allowing an erection. They are not painful, but it is important to respect the dosage prescribed by the doctor. Using too high a dose can cause an erection that is too intense and too long ( priapism ) which is painful and can sometimes permanently damage the penis.
These drugs are usually prescribed to people for whom oral treatments are contraindicated or have proven ineffective. They are covered by health insurance (15% for the cream and 30% for intracavernous injections) in certain cases ( multiple sclerosis, paraplegia, nerve damage linked to diabetes, etc.) as part of the exceptional drug procedure.
The cream treatment acts quickly (in 5 to 30 minutes) by causing an erection for 1 to 2 hours depending on the man. It comes in a single-dose container. The entire contents of the single-dose container should be applied to the tip of the penis. It should not be used more than 2 to 3 times a week, nor more than once every 24 hours. It may cause local side effects, including vaginal irritation in the partner. The use of condoms is recommended.
Intracavernous injection treatment is contraindicated in cases of predisposition to priapism due to certain diseases such as sickle cell disease or leukemia. In 90% of cases, the erection obtained allows penetration for up to an hour. Intracavernous self-injection, which consists of injecting the medication into the penis yourself, is possible after training in the injection technique.
The first injection should be performed by the doctor in the medical office to determine the specific dose that suits you and to teach you the injection technique, which you will then practice at home. The dose of product to be injected to cause an erection varies greatly from one person to another and should be adjusted gradually by a doctor familiar with this technique.
Adjunctive treatments

Yohimbine is an herbal substance that has been used for many years in the adjunctive treatment of erectile dysfunction. Its mechanism of action is poorly understood and the available data do not allow its effectiveness to be assessed. Only one Yohimbine-based medication is still available. It must be taken every day and its effect may only appear after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment. Since the marketing of oral medications is to be taken before sexual intercourse, its use is rarer.
Its side effects are anxiety, irritability, digestive disorders, dizziness, headaches, skin redness, and insomnia.
Non-drug treatments
Non-drug solutions can be offered when the man does not wish to take medication or when it is contraindicated for him.
The vacuum pump (also called vacuum)
It is a device comprising a cylinder placed on the penis and in which the patient creates a vacuum using a manual or electric pump. The suction of air into the device allows a flow of blood causing an erection which is maintained, after removing the cylinder, thanks to an elastic ring placed at the base of the penis. The ring should not be kept in place for more than 30 minutes. Adverse effects are minimal, including pain, a sensation of a cold penis and difficulty ejaculating.
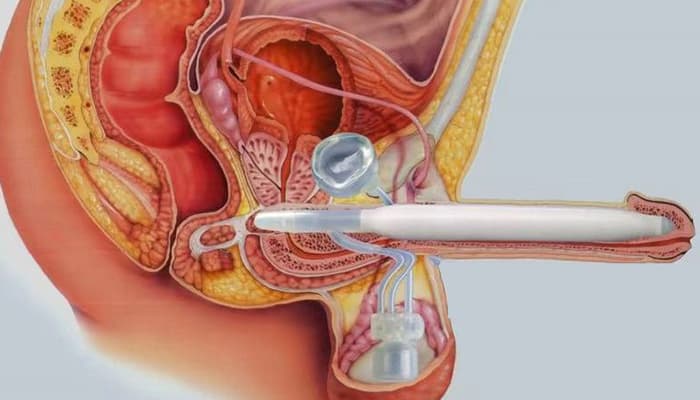
Penile prostheses
This is a definitive solution requiring surgery under general or local anesthesia. It is usually reserved for men who have severe and irreversible disorders for which other treatments have failed or cannot be used.
Penile prostheses are medical devices placed in the corpora cavernosa of the penis. They are of different types: rigid, semi-rigid or malleable, and inflatable. Their use may require training. The risks associated with the installation of these penile prostheses are mainly mechanical failures and risks of infection of the material (1 to 5% of cases) which often require the removal of the prosthesis.
Revascularization surgery
Penile revascularization surgery involves performing arterial bypasses to improve blood flow and pressure in the corpora cavernosa. This microsurgery is only intended for certain patients, for example, young patients who have injuries following trauma.
